Last Updated : 23 Mar, 2023
Improve
Postorder traversal is defined as a type of tree traversal which follows the Left-Right-Root policy such that for each node:
- The left subtree is traversed first
- Then the right subtree is traversed
- Finally, the root node of the subtree is traversed

Postorder traversal
Algorithm for Postorder Traversal of Binary Tree:
The algorithm for postorder traversal is shown as follows:
Postorder(root):
- Follow step 2 to 4 until root != NULL
- Postorder (root -> left)
- Postorder (root -> right)
- Write root -> data
- End loop
How does Postorder Traversal of Binary Tree Work?
Consider the following tree:

Example of Binary Tree
If we perform a postorder traversal in this binary tree, then the traversal will be as follows:
Step 1: The traversal will go from 1 to its left subtree i.e., 2, then from 2 to its left subtree root, i.e., 4. Now 4 has no subtree, so it will be visited.
Node 4 is visited
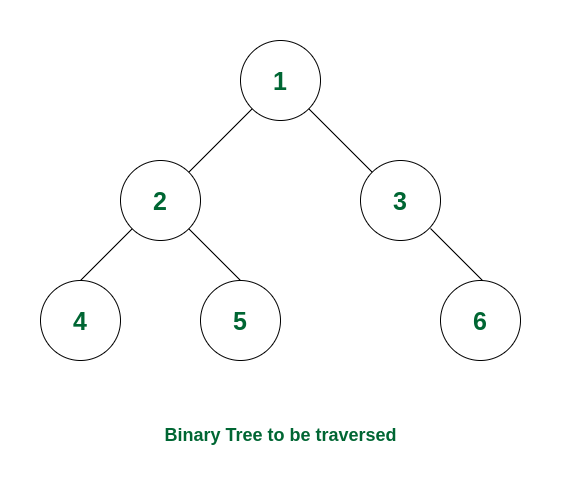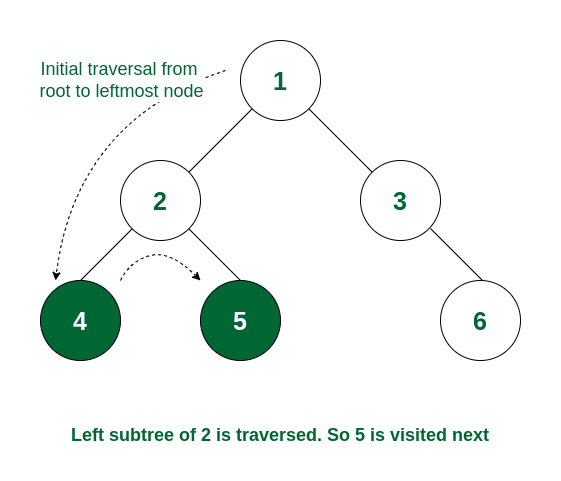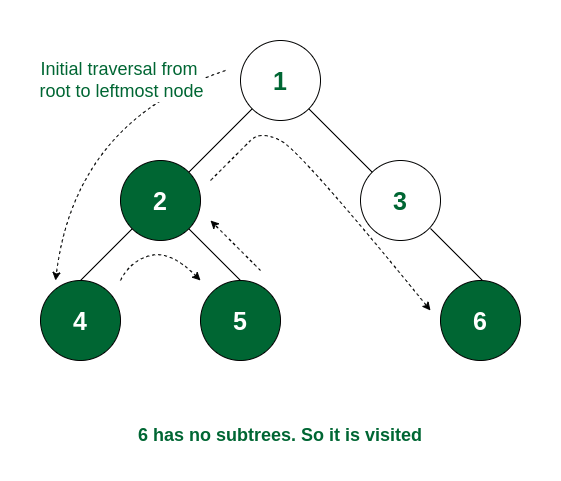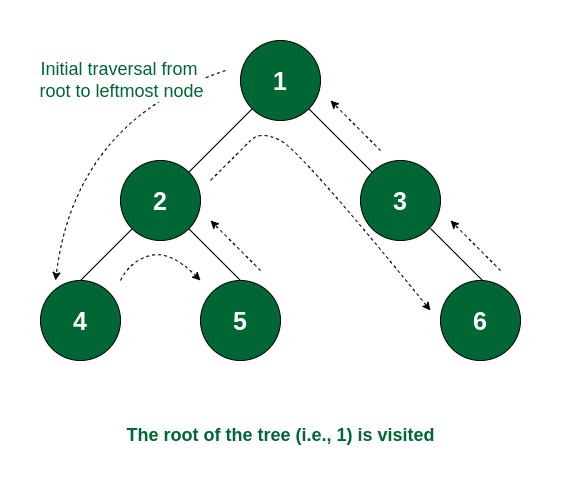
Step 2: As the left subtree of 2 is visited completely, now it will traverse the right subtree of 2 i.e., it will move to 5. As there is no subtree of 5, it will be visited.
Node 5 is visited
Step 3: Now both the left and right subtrees of node 2 are visited. So now visit node 2 itself.
Node 2 is visited
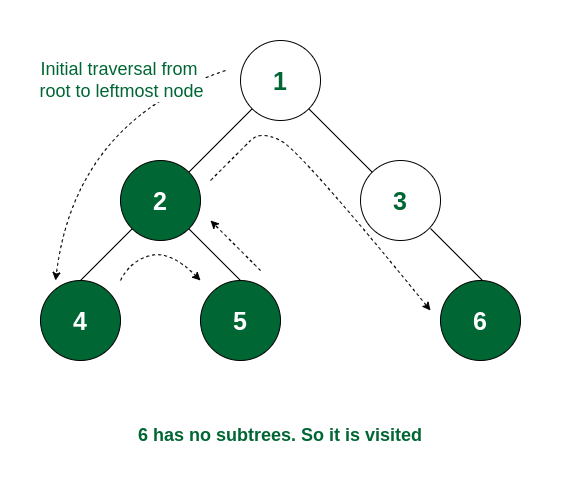
Step 4: As the left subtree of node 1 is traversed, it will now move to the right subtree root, i.e., 3. Node 3 does not have any left subtree, so it will traverse the right subtree i.e., 6. Node 6 has no subtree and so it is visited.
Node 6 is visited
Step 5: All the subtrees of node 3 are traversed. So now node 3 is visited.
Node 3 is visited
Step 6: As all the subtrees of node 1 are traversed, now it is time for node 1 to be visited and the traversal ends after that as the whole tree is traversed.
The complete tree is visited
So the order of traversal of nodes is 4 -> 5 -> 2 -> 6 -> 3 -> 1.
Program to implement Postorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Below is the code implementation of the postorder traversal:
C++
// C++ program for postorder traversals
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int v)
{
data = v;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to print postorder traversal
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// Now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->right = new Node(6);
// Function call
cout << "Postorder traversal of binary tree is: \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for postorder traversals
import java.util.*;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int v)
{
data = v;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to print postorder traversal
static void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
System.out.println("Postorder traversal of binary tree is: ");
printPostorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by prasad264
Python3
# Python program for postorder traversals
# Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, v):
self.data = v
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print postorder traversal
def printPostorder(node):
if node == None:
return
# First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left)
# Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right)
# Now deal with the node
print(node.data, end=' ')
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(6)
# Function call
print("Postorder traversal of binary tree is:")
printPostorder(root)
C#
// C# program for postorder traversals
using System;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int v)
{
data = v;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class GFG {
// Function to print postorder traversal
static void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
}
static public void Main()
{
// Code
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(
"Postorder traversal of binary tree is: ");
printPostorder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by karthik.
Javascript
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node {
constructor(v) {
this.data = v;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Function to print postorder traversal
function printPostorder(node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node
console.log(node.data + " ");
}
// Driver code
function main() {
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
// Function call
console.log("Postorder traversal of binary tree is: \n");
printPostorder(root);
}
main();
Output
Postorder traversal of binary tree is: 4 5 2 6 3 1
Explanation:
How postorder traversal works
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the total number of nodes. Because it traverses all the nodes at least once.
Auxiliary Space: O(1) if no recursion stack space is considered. Otherwise, O(h) where h is the height of the tree
- In the worst case, h can be the same as N (when the tree is a skewed tree)
- In the best case, h can be the same as logN (when the tree is a complete tree)
Use cases of Postorder Traversal:
Some use cases of postorder traversal are:
- This is used for tree deletion.
- It is also useful to get the postfix expression from an expression tree.
Related articles:
- Types of Tree traversals
- Iterative Postorder traversal (using two stacks)
- Iterative Postorder traversal (using one stack)
- Postorder of Binary Tree without recursion and without stack
- Find Postorder traversal of BST from preorder traversal
- Morris traversal for Postorder
- Print postorder traversal from preoreder and inorder traversal
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Previous
Largest sub-tree having equal no of 1's and 0's
Next
Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Share your thoughts in the comments